Most “normal” people may be more concerned about whether their walking posture is elegant or confident but rarely think how painful and tiresome this simple task is for people with disabilities. However, for patients with muscular dystrophy, walking is not only a challenge but can also fall suddenly leading to even more danger. They also suffer from standing difficulty which has become the normfor many of these patients. The most envious of the patients is to be able to walk like those unaffected and lead normal school, work, and social lives.
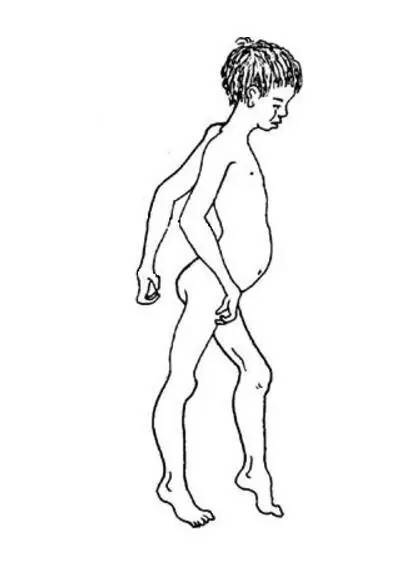
Muscular dystrophy is a group of primary skeletal muscle diseases caused by genetic factors. The main clinical manifestations of the disease are slow progressive muscle atrophy, muscle weakness and different levels of movement disorders. Among various types of muscular dystrophy, Duchenne (DMD) has the highest incidence, with one out of 3,600 patients being afflicted by DMD. DMD is serious; people are often disabled in their early years and DMD can lead to death. DMD is the most representative disease of hereditary muscular dystrophy.
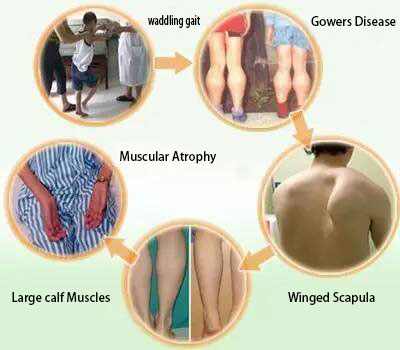
Skeletal muscle is one of the most abundant tissues in the human body and is also the main catalyst of movement, containing a large number of mature muscle cells that can differentiate into myoblast. Myoblast can merge with each other to become multinucleated muscle fibers and is the formation of the basic structure of skeletal muscle. Because genetic factors of DMD patients cause morphological and structural abnormalities of muscle cells, muscle cell damage, irreversible necrosis or even disappearance of muscle fibers, which leads to muscle atrophy, decreasing muscle stem cells, and the inability to repair damaged muscle tissue. This forms a vicious spiral. Finally, patients with systemic muscle atrophy typically die due to respiratory failure or heart failure.
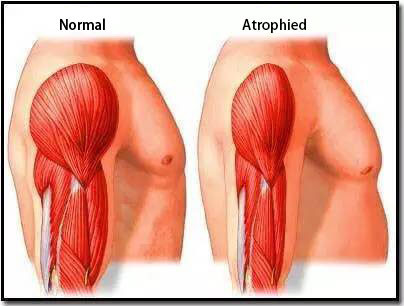
If stem cells are implanted in the muscle of muscular dystrophy patients, the development and differentiation of the formation of new healthy muscle fibers will replace the original atrophy of muscle fibers, and then the patient’s muscle is likely to regain strength. In recent years, applications of stem cell treatment in ischemic heart disease, ischemic lower limb vascular disease, osteonecrosis of femoral head (ONFH), spinal cord injury and other serious diseases has a remarkable curative effect. Whether stem cells can be used to replenish and repair the damaged muscle cells has become an outstanding subject.
In recent years, the research results show that mesenchymal stem cells can be induced to differentiate into muscle cells in vitro. In 1998, it was the first time to prove that bone marrow derived cells were able to replenish the damaged muscle from the circulation and participation in the repair of muscle, which provides a theoretical basis for the treatment of muscular dystrophy. In addition of self renewal and proliferation, mesenchymal stem cells also have controlled yet large differential potential and low immunity, and is an ideal stem cell transplantation cell type in the treatment of progressive muscular dystrophy.
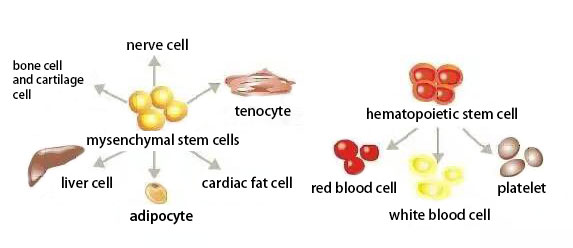
When mesenchymal stem cells are transplanted into the patient, the blood circulation is improved by secreting a large number of cytokines to repair the damaged muscle cells. Cytokines can also repair the damaged muscle membrane, correct defective expression of functional protein, repair the injured nerve, strengthen the communication signal, inhibit or reduce muscle cells lesions, increase volume, strength, functions of the muscle, while repairing the damaged muscle tissue continuously. MSCs can be differentiated into small amount of muscle cells to improve the patients’ muscle strength and replenish or replace muscle stem cells.
In 2010, the China General Practice published an article about mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of the clinical curative effect of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. From June 2007 to March 2009, 218 out of 269 cases (81%) of DMD patients with stem cell treatment had improvement on muscle strength after transplantation. Walking distance was extended. Action was more flexible. Acra was warm. Appetite was improved. Life qualities of the patients were improved. No adverse reaction and ethical controversy was found during the treatment due to the cell type and source. Stem cell therapy can delay the progression of the disease and improve life quality of the patients. It’s an effective method for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Stem cell therapy has led to a revolution in the world of medicine. With the deepening of research, it is found that stem cell therapy has an incomparable advantage comparing to the past routine of medical treatment. Although there is still a lack of large sample data, we believe that stem cell and general cell therapy technology will become a conventional therapy as surgery after drug treatment in the future.